
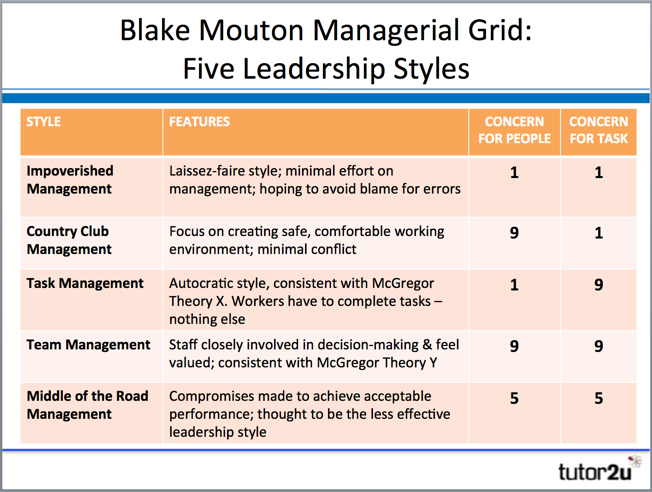
The leader is placed in the managerial grid, and it takes into account only two dimensions. The leader’s concern for production is placed on the X-axis and the second dimension is concerned for people, also sometimes called staff it is placed on the Y-axis. When deciding how best to accomplish a task, the two axes are both numbered from 1 to 9. Robert Blake and Mouton generated a grid that scales from 1-9 in terms of focusing on the task and focusing on people shown below. Robert Blake and Mouton develop this theory in 1964, and it considers the focus of managers when leading an organization, whether it’s on people or task. It also differs from Tannenbaum Schmidt, who focused more on managers and subordinates’ power and decision-making level.

They wanted to give a more nuanced picture of the leader than you get by using McGregor’s X and Y theory. The Blake and Mouton Managerial Grid came into existence when Blake and Mouton were hired as consultants by Exxon. It plots the degree of task-centeredness (X-Axis) versus people-centeredness (Y-Axis) to identify five leadership combinations as distinct leadership styles. The model is often called the Leadership Grid or Managerial Grid. Criticism of Blake and Mouton Managerial Grid Theory Blake and Mouton Managerial Grid Theoryīlake And Mouton Managerial Grid Theory is a popular model for thinking about leadership styles based on ‘ task versus person’ orientation and was designed by Robert Blake and Jane Mouton in 1964.Blake and Mouton Managerial Grid Example.Middle of the road leadership -Leadership style 5.5.Produce or Perish leadership (Leadership style 9.1).

Country Club leadership (Leadership style 1.9).Blake and Mouton Managerial Grid 5 Leadership Styles.Archie Carroll’s CSR Pyramid | Corporate Social Responsibility Pyramid.Vroom-Yetton Decision-Making Model | Vroom Yetton Model Pros and Cons.Max Weber Six Principles Of Bureaucracy.Blake and Mouton Managerial Grid Theory.

Blake and Mouton Managerial Grid Theory | Leadership Style Grid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
